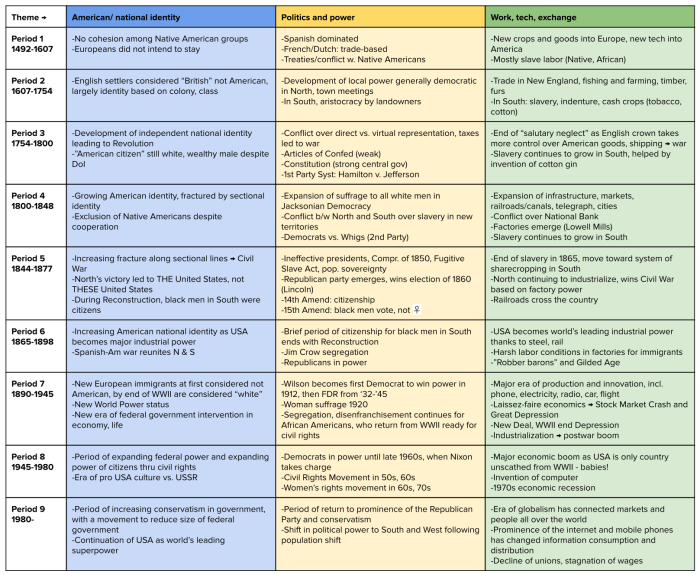
AP World History Unit 5 notes provide an in-depth examination of the period from 1450 to 1750, a time of profound global change and interconnectedness. From the rise of empires to the birth of new technologies, this unit offers a fascinating exploration of the forces that shaped the modern world.
As we delve into these notes, we will uncover the key themes and ideas that defined this era, examining the major events and developments that shaped the course of human history.
Key Concepts
Unit 5 of AP World History delves into the profound transformations that shaped the global landscape during the period from 1200 to 1450 CE. This era witnessed the rise and fall of empires, the spread of new technologies and ideas, and the emergence of global trade networks that connected civilizations across vast distances.
Key themes and ideas that permeate this unit include:
- The rise of large, centralized states and empires, such as the Mongol Empire and the Ming Dynasty in China.
- The spread of new technologies, including the compass, gunpowder, and the printing press, which transformed warfare, communication, and knowledge dissemination.
- The growth of trade and the emergence of global trade networks, particularly along the Silk Road and the Indian Ocean trade routes.
- The rise of new religious movements, such as Islam and Christianity, and their impact on societies and cultures worldwide.
li>The exchange of ideas and technologies between different civilizations, leading to cultural diffusion and the development of new artistic and intellectual traditions.
The Rise of Empires
During this period, several large, centralized empires emerged and dominated vast regions of the world. The Mongol Empire, founded by Genghis Khan, was the largest contiguous land empire in history, stretching from Eastern Europe to the Pacific Ocean.
The Ming Dynasty in China, established in 1368 CE, was another powerful empire that oversaw a period of cultural and economic prosperity. These empires played a significant role in shaping the political, economic, and cultural landscapes of their respective regions.
Historical Periods
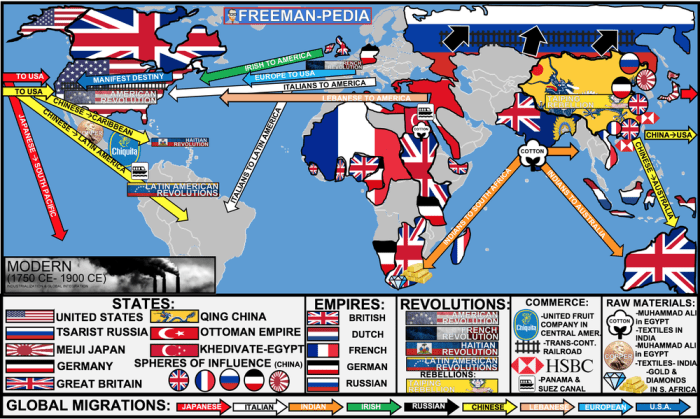
AP World History Unit 5 encompasses several distinct historical periods, each characterized by unique features and events that shaped the course of world history.
These periods include the following:
Early Civilizations (c. 3500-c. 500 BCE)
This period witnessed the emergence of the first complex societies and the development of writing, agriculture, and urban centers. Notable civilizations of this era include Mesopotamia, Egypt, the Indus Valley, and China.
Classical Civilizations (c. 500-c. 300 BCE)
This period saw the rise of powerful empires and the development of sophisticated political systems, philosophies, and artistic traditions. Key civilizations of this era include Greece, Rome, Persia, and India.
Post-Classical Civilizations (c. 300-c. 1450 CE)
This period was marked by the expansion of trade and cultural exchange, the rise of new religious movements, and the development of feudal systems. Significant civilizations of this era include the Byzantine Empire, the Islamic caliphates, and the Mongol Empire.
Early Modern World (c. 1450-c. 1750 CE)
This period witnessed the European Age of Exploration, the rise of mercantilism, and the establishment of global trade networks. Key events of this era include the voyages of Christopher Columbus and the establishment of European colonies in the Americas.
After reviewing AP World History Unit 5 notes, I stumbled upon an intriguing article about the Wild West Showman NFL Team . Their unique style of play reminded me of the nomadic empires we studied in Unit 5, who often relied on mobility and adaptability.
Returning to my notes, I couldn’t help but draw parallels between the team’s strategies and the tactics employed by ancient civilizations.
Late Modern World (c. 1750-c. 1914 CE)
This period was characterized by the Industrial Revolution, the rise of nationalism, and the expansion of European empires. Key events of this era include the American Revolution, the French Revolution, and the Industrial Revolution.
Twentieth Century (c. 1914-c. 2000 CE)
This period witnessed two world wars, the rise of fascism and communism, and the process of decolonization. Key events of this era include World War I, World War II, and the Cold War.
Global Interactions
During the time period covered in AP World History Unit 5, the world witnessed a surge in interactions between different regions. These interactions had profound economic, political, and cultural consequences, shaping the course of human history.
Economically, the growth of trade networks and the exchange of goods and ideas led to the development of new technologies, the expansion of markets, and the rise of global capitalism. The Columbian Exchange, for instance, introduced new crops and livestock to both the Americas and Europe, transforming diets and agricultural practices worldwide.
Political Interactions
Politically, global interactions often involved conflict and competition. European powers, driven by mercantilism and the search for resources, established colonies in Africa, Asia, and the Americas. This led to the rise of imperialism and the subjugation of indigenous peoples.
However, global interactions also fostered cooperation and diplomacy. The Silk Road, a vast network of trade routes connecting East Asia to Europe, facilitated the exchange of ideas and technologies between different civilizations.
Cultural Interactions
Culturally, global interactions resulted in the spread of religions, artistic styles, and scientific knowledge. The spread of Buddhism from India to China and Japan, for example, had a profound impact on the development of Asian cultures. Similarly, the Renaissance in Europe was influenced by the rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman texts.
These global interactions created a more interconnected and interdependent world, laying the foundation for the globalization that characterizes the modern era.
Technological Advancements
The time period covered in AP World History Unit 5 witnessed significant technological advancements that profoundly impacted societies and cultures.
These advancements included the development of new tools, techniques, and materials, which led to increased agricultural productivity, improved transportation and communication, and the rise of new industries.
Agriculture
Technological advancements in agriculture, such as the development of new farming techniques, irrigation systems, and crop varieties, led to increased food production and population growth.
- The invention of the plow allowed farmers to cultivate larger areas of land, increasing crop yields.
- The development of irrigation systems, such as canals and dams, enabled farmers to control water supply and expand agricultural production into arid regions.
- The introduction of new crops, such as rice and wheat, provided a more diverse and nutritious food supply.
Transportation and Communication
Technological advancements in transportation and communication, such as the development of new modes of transport and communication networks, facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and people.
- The invention of the wheel and the sail revolutionized transportation, allowing for faster and more efficient movement of goods and people.
- The development of roads and bridges improved connectivity between different regions, fostering trade and cultural exchange.
- The invention of the printing press and the development of postal systems facilitated the spread of knowledge and ideas, contributing to the rise of literacy and the dissemination of information.
Industry
Technological advancements in industry, such as the development of new machines and manufacturing techniques, led to increased production and economic growth.
- The invention of the steam engine provided a new source of power for factories, enabling the mechanization of production and the rise of industrialization.
- The development of new machinery, such as the cotton gin and the power loom, increased the efficiency of textile production, leading to a boom in the textile industry.
- The invention of the telegraph and the telephone revolutionized communication, facilitating the coordination of business activities and the spread of information.
Social and Cultural Changes
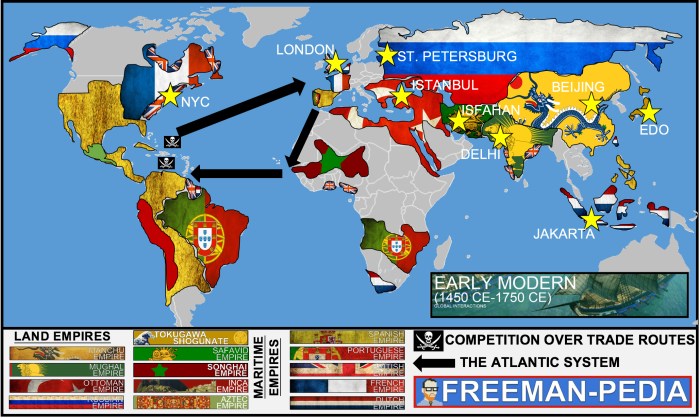
During the time period covered in AP World History Unit 5, several significant social and cultural changes occurred, shaping the course of human history. These changes were driven by various factors, including economic transformations, technological advancements, and political upheavals.The rise of agricultural societies and the development of cities led to the emergence of complex social hierarchies and the specialization of labor.
This resulted in the development of social classes, with elites wielding power and influence over commoners. The growth of trade and commerce facilitated the spread of ideas, goods, and cultural practices across vast distances, leading to cultural exchange and the emergence of new cultural identities.
Changing Family Structures
The traditional patriarchal family structure, which had been prevalent in many societies, began to undergo changes. In some regions, women gained greater autonomy and influence within the family, while in others, the extended family system weakened, giving way to smaller nuclear families.
These shifts were influenced by economic factors, such as the rise of wage labor, and by social and cultural movements that challenged traditional gender roles.
Spread of Religious Beliefs
The spread of major religions, such as Christianity, Islam, and Buddhism, had a profound impact on societies around the world. These religions provided spiritual guidance, moral codes, and a sense of community to their followers. The expansion of religious networks also facilitated the exchange of ideas and cultural practices, contributing to the development of new cultural traditions and identities.
Artistic and Intellectual Achievements
The period witnessed remarkable artistic and intellectual achievements across different regions. In Europe, the Renaissance and Reformation sparked a renewed interest in classical learning, humanism, and the arts. In China, the Song dynasty saw the flourishing of Confucianism and the development of new artistic styles in painting and literature.
The Islamic world witnessed the rise of renowned scholars and scientists, who made significant contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine.
Consequences of Social and Cultural Changes
These social and cultural changes had far-reaching consequences for societies around the world. The rise of social hierarchies and the specialization of labor led to increased inequality and the emergence of social conflicts. The spread of religious beliefs shaped political and social institutions, often leading to the establishment of religious states and the persecution of dissenters.
Artistic and intellectual achievements enriched human culture and contributed to the advancement of knowledge and civilization.The social and cultural changes that occurred during this period laid the foundation for the development of modern societies and continue to shape the world we live in today.
Understanding these changes is crucial for comprehending the complexities of human history and the interconnectedness of different cultures and civilizations.
Empires and States
The rise and fall of empires and states have shaped the course of human history. In AP World History Unit 5, we will examine the factors that contributed to the success and decline of these powerful entities.
Factors Contributing to the Rise of Empires, Ap world history unit 5 notes
-
-*Military Strength
Empires often expanded through conquest, relying on superior military technology and organization.
-*Economic Prosperity
A strong economy provided the resources necessary for military campaigns and the maintenance of a vast territory.
-*Political Stability
Effective leadership and a stable political system ensured the continuity and coherence of the empire.
-*Cultural Unity
A shared culture and ideology fostered loyalty and cohesion among the empire’s diverse populations.
Factors Contributing to the Decline of Empires
-
-*Internal Strife
Civil wars, rebellions, and political instability weakened the empire from within.
-*External Pressures
Invasions, natural disasters, and economic challenges could overwhelm the empire’s defenses.
-*Overextension
Empires often stretched too far, making it difficult to control and defend their vast territories.
-*Economic Decline
Economic stagnation or inflation could cripple the empire’s ability to sustain itself.
Primary Sources: Ap World History Unit 5 Notes
Primary sources provide direct access to the past and offer valuable insights into the time period covered in AP World History Unit 5. These sources can include written documents, such as letters, diaries, and official records, as well as physical artifacts, such as tools, weapons, and art.
Strengths of Primary Sources
-
-*Authenticity
Primary sources provide firsthand accounts of events and experiences, offering a direct connection to the past.
-*Detail
They often contain rich and specific information that can help historians understand the complexities of the time period.
-*Objectivity
While not completely unbiased, primary sources can provide a more objective perspective than secondary sources, which are often influenced by the author’s interpretation.
Weaknesses of Primary Sources
-
-*Incomplete
Primary sources may not provide a complete picture of the past, as they are often fragmentary or incomplete.
-*Bias
Primary sources can be biased towards certain perspectives or interests, making it important to consider their context and limitations.
-*Interpretation
Understanding and interpreting primary sources requires careful analysis and consideration of their historical context.
Historical Interpretations
Various historical interpretations exist regarding the time period covered in AP World History Unit 5. These interpretations stem from different perspectives, methodologies, and evidence used by historians.
One interpretation emphasizes the role of economic factors in shaping historical developments. This interpretation argues that economic changes, such as the growth of trade and the emergence of capitalism, played a significant role in the political, social, and cultural transformations of the period.
Political Factors
Another interpretation focuses on the influence of political factors, such as the rise of nation-states and the expansion of empires. This interpretation argues that political decisions and actions had a profound impact on the course of history during this time period.
Cultural Factors
A third interpretation highlights the importance of cultural factors, such as the spread of ideas and the development of new technologies. This interpretation argues that cultural exchanges and advancements had a significant influence on the societies and civilizations of the period.
The evidence supporting each of these interpretations varies. Economic historians often point to data on trade volumes, market expansion, and the growth of industries. Political historians cite documents such as treaties, laws, and diplomatic correspondence. Cultural historians examine sources such as literature, art, and religious texts.
FAQ Insights
What are the key themes covered in AP World History Unit 5?
The key themes include global interactions, technological advancements, social and cultural changes, and the rise and fall of empires.
What are some examples of significant events in this period?
Some examples include the voyages of exploration, the Protestant Reformation, and the Scientific Revolution.
How did global interactions shape the world during this time?
Global interactions led to the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, contributing to cultural diffusion and economic growth.
What were some of the major technological advancements of this era?
Major technological advancements included the development of the printing press, the compass, and new methods of shipbuilding.