Delve into the intricacies of chemistry with the Periodic Table Chapter 6 Answer Key, a comprehensive resource that illuminates the fundamental concepts of the periodic table and its profound implications in various scientific disciplines.
This guide provides a structured exploration of the chapter’s key themes, including periodic trends, chemical bonding, chemical reactions, and the multifaceted applications of the periodic table. Through a blend of clear explanations, illustrative examples, and engaging insights, it empowers learners to grasp the essence of this cornerstone of chemistry.
Chapter Overview
Chapter 6 of the Periodic Table covers the fundamental principles and applications of the periodic table, a systematic arrangement of elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties.
Key points:
- The periodic table organizes elements into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows) based on their atomic number.
- Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to having the same number of valence electrons.
- The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of elements and their reactivity.
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends are patterns in the properties of elements as we move across periods and down groups in the periodic table.
Key trends include:
- Atomic radius: Generally decreases across a period from left to right and increases down a group.
- Ionization energy: Generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group.
- Electronegativity: Generally increases across a period from left to right and decreases down a group.
These trends can be used to predict the properties of elements and their reactivity.
Chemical Bonding, The periodic table chapter 6 answer key
Chemical bonding is the force that holds atoms together to form molecules and compounds.
Types of chemical bonds include:
- Ionic bonding: Formed between a metal and a nonmetal, where electrons are transferred from the metal to the nonmetal.
- Covalent bonding: Formed between two nonmetals, where electrons are shared between the atoms.
- Metallic bonding: Formed between metal atoms, where electrons are delocalized and move freely throughout the metal.
The periodic table can be used to predict the type of bond that will form between two elements based on their position in the table.
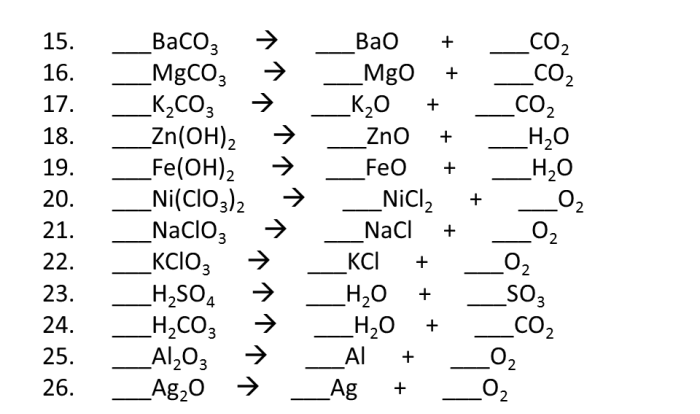
Chemical Reactions
Chemical reactions are processes that involve the rearrangement of atoms and molecules to form new substances.
Types of chemical reactions include:
- Acid-base reactions: Reactions between an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of a salt and water.
- Redox reactions: Reactions involving the transfer of electrons between atoms or molecules.
- Precipitation reactions: Reactions between two solutions that result in the formation of an insoluble solid.
The periodic table can be used to predict the products of a chemical reaction based on the reactivity of the elements involved.
Applications of the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a valuable tool in various fields, including:
- Chemistry: Predicting the properties and reactivity of elements and compounds.
- Physics: Understanding the electronic structure and behavior of atoms.
- Materials science: Designing and developing new materials with specific properties.
The periodic table is a fundamental tool for understanding the properties of matter and predicting the outcome of chemical reactions.
Answers to Common Questions: The Periodic Table Chapter 6 Answer Key
What are the key concepts covered in Chapter 6 of the Periodic Table?
Chapter 6 of the Periodic Table covers periodic trends, chemical bonding, chemical reactions, and the applications of the periodic table.
How can the periodic table be used to predict the properties of elements?
The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of elements based on their position in the table. For example, elements in the same group tend to have similar chemical properties.
What are the different types of chemical bonds?
The different types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
How can the periodic table be used to predict the type of bond that will form between two elements?
The periodic table can be used to predict the type of bond that will form between two elements based on their electronegativity difference.