Welcome to the fascinating realm of cell biology, where we delve into the intricate world of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. This comprehensive guide, “Cell Biology Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Coloring Worksheet Answers,” serves as an invaluable resource for students and educators alike, providing a deeper understanding of the fundamental differences and similarities between these two distinct cell types.
Through engaging visuals, clear explanations, and thought-provoking questions, this guide empowers you to grasp the essential concepts of cell biology. Dive into the vibrant world of cells and discover the secrets that govern their structure, function, and role in shaping life as we know it.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
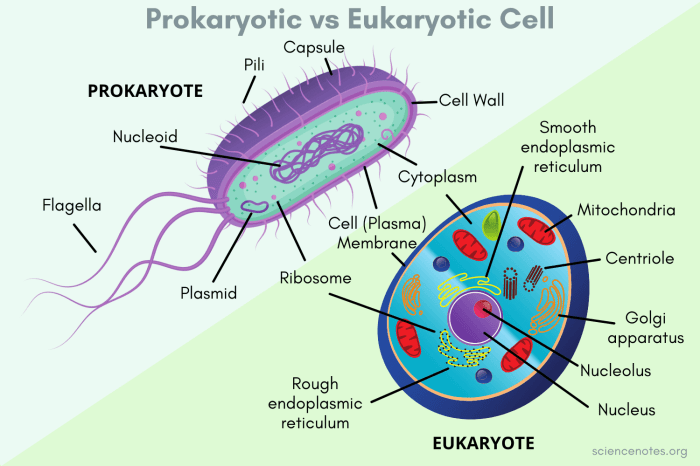
Cells are the basic unit of life and can be classified into two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells and lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles that perform specific functions.
Key Characteristics of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
| Feature | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Nucleus | Absent | Present |
| Membrane-bound organelles | Absent | Present |
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Cell wall | Present (in most cases) | Present (in plants and fungi only) |
| Examples | Bacteria, archaea | Animals, plants, fungi, protists |
Cell Biology Coloring Worksheet: Cell Biology Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Coloring Worksheet Answers
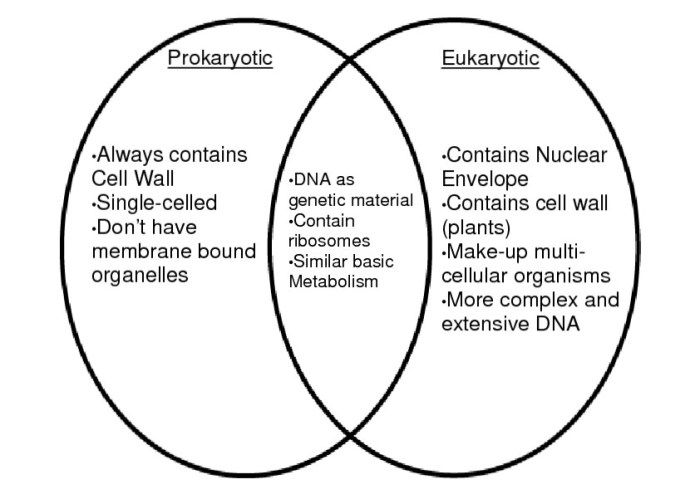
Coloring worksheets are a valuable tool for studying cell biology because they allow students to visualize and learn about different cell structures and functions in a hands-on way. By coloring different parts of the cell, students can better understand their shape, location, and role in the cell’s overall function.
Sample Coloring Worksheet: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Instructions:
- Color the nucleus of the eukaryotic cell blue.
- Color the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cell pink.
- Color the cell membrane of the eukaryotic cell green.
- Color the ribosomes of the prokaryotic cell red.
- Color the cell wall of the prokaryotic cell brown.
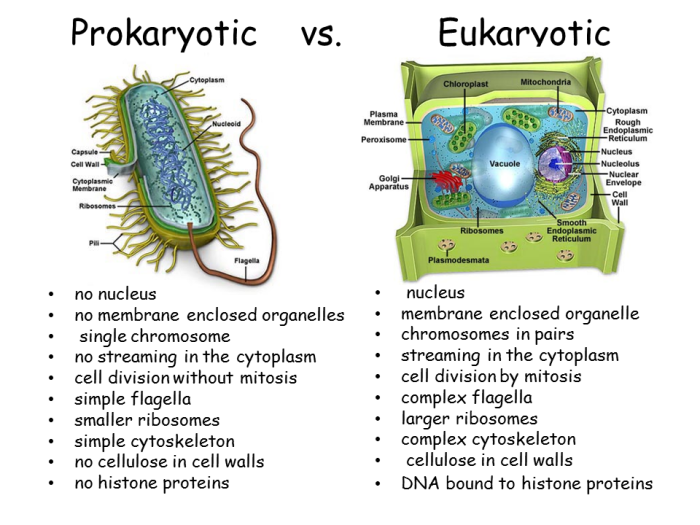
Cell Organelles

Cells contain a variety of organelles, each of which performs a specific function. The major organelles found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells include:
Organelles by Function
| Function | Organelle |
|---|---|
| Protein synthesis | Ribosomes |
| Energy production | Mitochondria (eukaryotic cells only) |
| Photosynthesis | Chloroplasts (plant cells only) |
| Waste removal | Lysosomes (eukaryotic cells only) |
| Transport | Golgi apparatus (eukaryotic cells only) |
Cell Processes
Cells carry out a variety of essential processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and protein synthesis. These processes differ between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of their location and complexity.
Photosynthesis, Cell biology prokaryotes and eukaryotes coloring worksheet answers
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants and other organisms use sunlight to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. In prokaryotic cells, photosynthesis occurs in the plasma membrane. In eukaryotic cells, photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts.
Respiration
Respiration is the process by which cells use oxygen to break down glucose and produce energy. In prokaryotic cells, respiration occurs in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells, respiration occurs in the mitochondria.
Protein Synthesis
Protein synthesis is the process by which cells use amino acids to build proteins. In prokaryotic cells, protein synthesis occurs on ribosomes that are located in the cytoplasm. In eukaryotic cells, protein synthesis occurs on ribosomes that are located in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Common Queries
What is the primary difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess both.
What are the major organelles found in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and ribosomes.
How do prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells divide?
Prokaryotes divide through binary fission, while eukaryotes divide through mitosis or meiosis.
What is the significance of cell differentiation?
Cell differentiation allows multicellular organisms to develop specialized tissues and organs with distinct functions.
What are some practical applications of cell biology?
Cell biology has applications in medicine, biotechnology, agriculture, and environmental science.