Welcome to the comprehensive American History Reconstruction to the Present Textbook PDF, a captivating journey through the annals of American history from the Reconstruction Era to the modern-day. This meticulously crafted narrative unfolds with unparalleled depth and clarity, offering a profound understanding of the events, policies, and individuals that have shaped the nation.
From the transformative Reconstruction Era to the complexities of the present day, this textbook delves into the intricacies of American society, politics, and culture. It illuminates the triumphs and challenges, the turning points and the enduring legacies that have shaped the American experience.
Reconstruction Era: American History Reconstruction To The Present Textbook Pdf

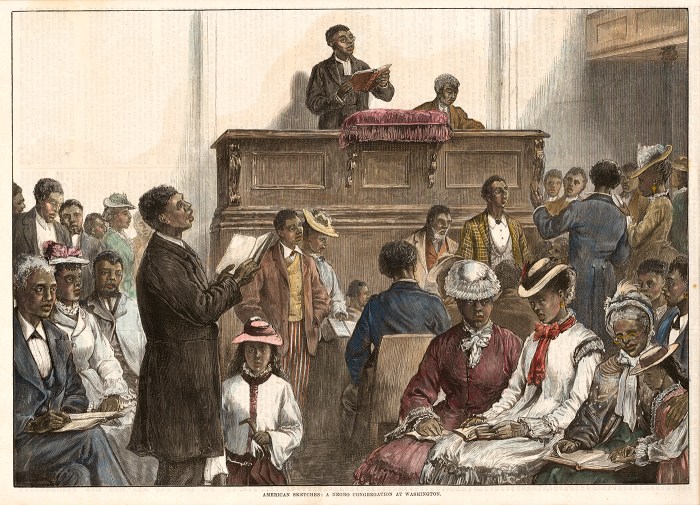
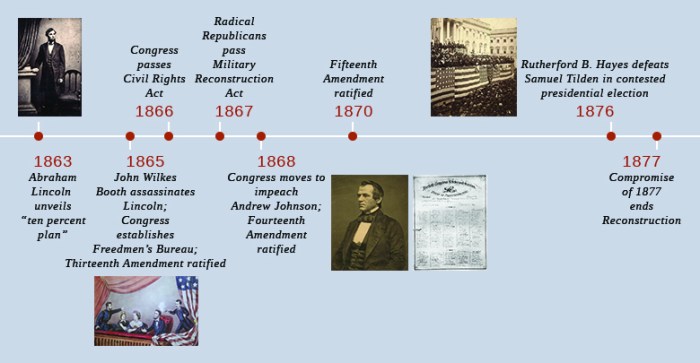
The Reconstruction Era (1865-1877) was a period of significant political, social, and economic change in the United States following the Civil War. The major goal of Reconstruction was to reunite the country and to address the legacy of slavery.
The Reconstruction Era was marked by the passage of several key amendments to the Constitution, including the Thirteenth Amendment (abolishing slavery), the Fourteenth Amendment (granting citizenship to all persons born or naturalized in the United States), and the Fifteenth Amendment (prohibiting states from depriving citizens the right to vote based on race).
The Reconstruction Era also saw the establishment of the Freedmen’s Bureau, which provided aid to freed slaves, and the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1866, which granted African Americans the same civil rights as white citizens.
The Reconstruction Era was a period of great progress for African Americans, but it was also a time of violence and resistance from white Southerners. The Ku Klux Klan, a white supremacist terrorist organization, emerged during this period and targeted African Americans and their white allies.
The Reconstruction Era ended in 1877 with the Compromise of 1877, which resulted in the withdrawal of federal troops from the South and the end of Reconstruction.
Impact of Reconstruction on American Society and Politics
The Reconstruction Era had a profound impact on American society and politics. The passage of the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth Amendments expanded the rights of African Americans and helped to lay the foundation for the civil rights movement of the 20th century.
The Reconstruction Era also led to the establishment of the Republican Party as the dominant party in the South. The Republican Party was supported by African Americans and white Northerners who believed in the principles of equality and civil rights.
The Reconstruction Era was a period of great change and upheaval in American history. It was a time of both progress and setbacks, but it ultimately helped to shape the United States into the country it is today.
The Gilded Age
The Gilded Age (1877-1900) was a period of rapid economic growth and industrialization in the United States. It was also a time of great social and political change.
The Gilded Age was marked by the rise of large corporations, the growth of cities, and the influx of immigrants from Europe.
Economic Changes
The Gilded Age was a time of great economic growth. The United States became the world’s leading industrial power, and the economy grew rapidly.
The growth of the economy was driven by a number of factors, including the development of new technologies, the expansion of railroads, and the exploitation of natural resources.
The Gilded Age also saw the rise of large corporations. Corporations were able to amass great wealth and power, and they played a major role in the economy.
Social Changes
The Gilded Age was a time of great social change. The growth of cities led to the emergence of a new urban working class.
The influx of immigrants from Europe also changed the social fabric of the United States. Immigrants brought with them their own cultures and traditions, and they helped to shape the American identity.
Political Changes
The Gilded Age was a time of great political change. The Republican Party dominated politics during this period, and the party was closely aligned with big business.
The Democratic Party was the main opposition party during the Gilded Age. The Democratic Party was supported by farmers, workers, and immigrants.
The Gilded Age was a time of great economic growth and social change. It was also a time of political upheaval.
Impact of the Gilded Age on American Society and Politics
The Gilded Age had a profound impact on American society and politics. The rise of large corporations and the growth of cities led to a number of social problems, including poverty, crime, and corruption.
The Gilded Age also saw the emergence of the Progressive movement, which sought to address the social problems of the time.
The Progressive movement was a major force in American politics during the early 20th century. The movement led to the passage of a number of reforms, including the Pure Food and Drug Act and the Clayton Antitrust Act.
The Gilded Age was a period of great change and upheaval in American history. It was a time of both progress and setbacks, but it ultimately helped to shape the United States into the country it is today.
The Progressive Era

The Progressive Era (1890-1920) was a period of social and political reform in the United States.
The Progressive movement was a response to the social and economic problems that emerged during the Gilded Age. These problems included poverty, crime, corruption, and the exploitation of workers.
The Progressive movement was led by a diverse group of people, including journalists, social workers, and politicians.
The Progressives believed that government could play a role in solving the social and economic problems of the time.
Major Reforms, American history reconstruction to the present textbook pdf
The Progressive Era saw the passage of a number of major reforms, including:
- The Pure Food and Drug Act (1906)
- The Clayton Antitrust Act (1914)
- The Federal Reserve Act (1913)
- The Seventeenth Amendment (1913)
- The Nineteenth Amendment (1920)
These reforms helped to improve the quality of life for many Americans. They also helped to make the government more responsive to the needs of the people.
Impact of the Progressive Era on American Society and Politics
The Progressive Era had a profound impact on American society and politics. The reforms that were passed during this period helped to improve the lives of many Americans.
The Progressive Era also helped to strengthen the role of government in American society. The government became more involved in regulating the economy and protecting the rights of workers.
The Progressive Era was a time of great change and upheaval in American history. It was a time of both progress and setbacks, but it ultimately helped to shape the United States into the country it is today.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the significance of the Reconstruction Era in American history?
The Reconstruction Era marked a transformative period in American history, characterized by efforts to rebuild the nation after the Civil War and integrate African Americans into society. It witnessed the passage of landmark amendments to the Constitution, including the Thirteenth, Fourteenth, and Fifteenth Amendments, which abolished slavery, granted citizenship to African Americans, and extended voting rights.
How did the Gilded Age impact American society?
The Gilded Age was a period of rapid economic growth and industrialization in the United States. It brought about significant changes in society, including the rise of large corporations, urbanization, and the influx of immigrants. However, this era was also marked by widespread inequality, social unrest, and political corruption.
What were the key reforms enacted during the Progressive Era?
The Progressive Era was a period of social and political reform in the United States. It witnessed the enactment of numerous reforms aimed at addressing the problems created by industrialization and urbanization. These reforms included the Pure Food and Drug Act, the Clayton Antitrust Act, and the establishment of the Federal Reserve System.
