Dna replication transcription translation lab worksheet – Embark on a scientific voyage with the DNA Replication, Transcription, and Translation Lab Worksheet, a comprehensive guide to the fundamental processes that underpin the very essence of life. Delve into the intricate mechanisms of DNA replication, transcription, and translation, unraveling the secrets of genetic inheritance and protein synthesis.
This meticulously crafted worksheet provides a hands-on approach to understanding the complexities of molecular biology, equipping students with a deep comprehension of the processes that govern gene expression and protein production.
DNA Replication

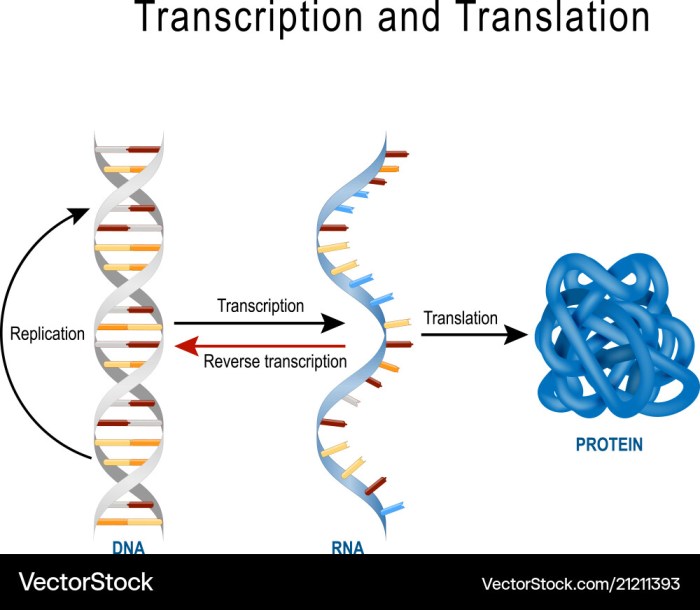
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes a copy of its DNA. This process is essential for cell division, as it ensures that each new cell has a complete copy of the genetic material.
The key enzymes involved in DNA replication are DNA polymerase, helicase, and ligase. DNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes the new DNA strand, helicase is the enzyme that unwinds the DNA double helix, and ligase is the enzyme that joins the newly synthesized DNA strands together.
The process of DNA replication begins with the unwinding of the DNA double helix by helicase. This creates a replication bubble, which is a region of the DNA where the two strands are separated. DNA polymerase then binds to the single-stranded DNA and begins to synthesize a new DNA strand.
The new DNA strand is synthesized in the 5′ to 3′ direction, and it is complementary to the template strand.
Once the new DNA strand has been synthesized, ligase joins the new strand to the existing DNA strand. This completes the process of DNA replication.
Transcription
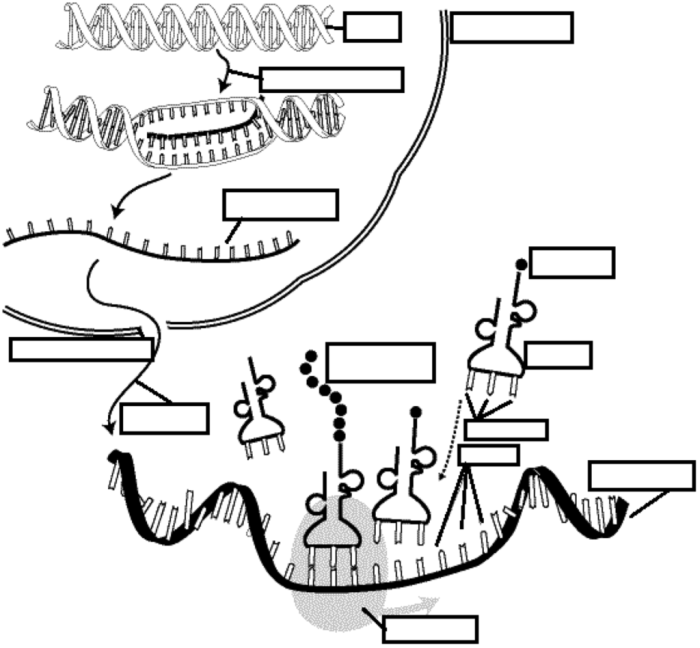
Transcription is the process by which a cell makes a copy of a gene in RNA. This process is essential for gene expression, as it allows the cell to produce the proteins that it needs.
The key enzymes involved in transcription are RNA polymerase, transcription factors, and RNA processing enzymes. RNA polymerase is the enzyme that synthesizes the new RNA strand, transcription factors are proteins that bind to DNA and help RNA polymerase to initiate transcription, and RNA processing enzymes are enzymes that modify the newly synthesized RNA strand.
The process of transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to the DNA template strand. RNA polymerase then unwinds the DNA double helix and begins to synthesize a new RNA strand. The new RNA strand is synthesized in the 5′ to 3′ direction, and it is complementary to the template strand.
Once the new RNA strand has been synthesized, it is processed by RNA processing enzymes. These enzymes may remove introns, add exons, and modify the RNA strand in other ways. The processed RNA strand is then ready to be translated into protein.
Translation
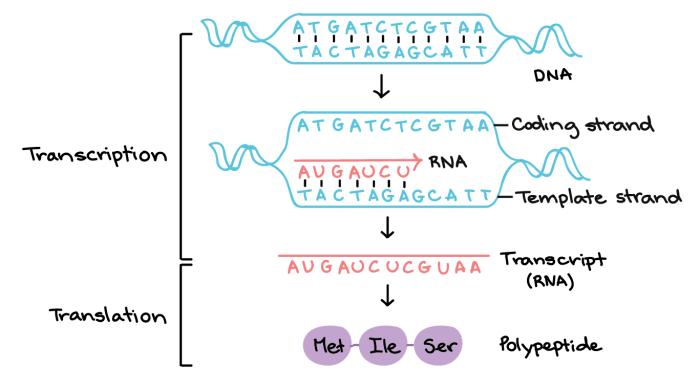
Translation is the process by which a cell uses the information in an RNA molecule to synthesize a protein. This process is essential for protein synthesis, as it allows the cell to produce the proteins that it needs.
The key components involved in translation are ribosomes, tRNA, and mRNA. Ribosomes are the structures that assemble the protein, tRNA is the molecule that carries the amino acids to the ribosome, and mRNA is the molecule that contains the genetic information for the protein.
The process of translation begins with the binding of a ribosome to the mRNA molecule. The ribosome then scans the mRNA molecule until it finds the start codon. The start codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that signals the ribosome to begin translation.
Once the ribosome has found the start codon, it begins to move along the mRNA molecule, reading the genetic information in groups of three nucleotides. Each group of three nucleotides is called a codon. The codon is then used to select the correct tRNA molecule, which carries the corresponding amino acid.
The amino acid is then added to the growing polypeptide chain. The ribosome continues to move along the mRNA molecule, reading the genetic information and adding amino acids to the polypeptide chain until it reaches a stop codon. The stop codon is a sequence of three nucleotides that signals the ribosome to stop translation.
Once the ribosome has reached a stop codon, it releases the polypeptide chain. The polypeptide chain then folds into its native conformation and becomes a functional protein.
Lab Worksheet: Dna Replication Transcription Translation Lab Worksheet
DNA Replication
- Explain the purpose of DNA replication.
- Describe the key enzymes involved in DNA replication.
- Discuss the process of DNA replication in detail.
Transcription
- Define transcription and explain its role in gene expression.
- Describe the key steps involved in transcription.
- Discuss the different types of RNA produced during transcription.
Translation
- Explain the purpose of translation and its role in protein synthesis.
- Describe the key steps involved in translation.
- Discuss the role of ribosomes and tRNA in translation.
| Feature | DNA Replication | Transcription | Translation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | To make a copy of DNA | To make a copy of a gene in RNA | To make a protein |
| Key enzymes | DNA polymerase, helicase, ligase | RNA polymerase, transcription factors, RNA processing enzymes | Ribosomes, tRNA, mRNA |
| Template | DNA | DNA | mRNA |
| Product | DNA | RNA | Protein |
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the purpose of DNA replication?
DNA replication ensures the accurate duplication of genetic material during cell division, ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information to daughter cells.
Describe the key steps involved in transcription.
Transcription involves three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination. During initiation, RNA polymerase binds to a specific DNA sequence called the promoter. Elongation involves the synthesis of an RNA molecule complementary to the DNA template strand. Termination occurs when RNA polymerase reaches a specific termination sequence.
What is the role of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes are essential for protein synthesis. They bind to mRNA and tRNA molecules and facilitate the decoding of the genetic code, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids in the growing polypeptide chain.