As two automobiles start together from the same place, they embark on a journey that showcases the interplay of motion, energy, and forces. This analysis delves into the intricate details of their movement, revealing the factors that influence their speed, acceleration, and displacement.
Our exploration begins with a detailed examination of the automobiles themselves, their specifications, and the environmental conditions that shape their performance. We then delve into the concepts of motion and speed, exploring the factors that determine their acceleration and velocity.
Through a comparative table, we visualize the differences in their performance over time.
Initial Conditions
Two automobiles, an older Toyota Camry and a newer Tesla Model S, start together from the same point on a flat, straight road. The Camry is a 2010 model with a 2.5-liter engine and a curb weight of 3,300 pounds.
The Tesla is a 2022 model with an electric motor and a curb weight of 4,500 pounds.
The starting point is at the intersection of two roads, and the weather is clear and dry. The road conditions are good, with no potholes or other obstacles.
Motion and Speed
The Camry accelerates from rest at a rate of 2.5 m/s 2, while the Tesla accelerates at a rate of 3.5 m/s 2. After 10 seconds, the Camry has reached a speed of 25 m/s, while the Tesla has reached a speed of 35 m/s.
The speed and acceleration of the two automobiles over time are shown in the following table:
| Time (s) | Camry Speed (m/s) | Tesla Speed (m/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 25 | 35 |
| 20 | 50 | 70 |
| 30 | 75 | 105 |
Distance and Displacement

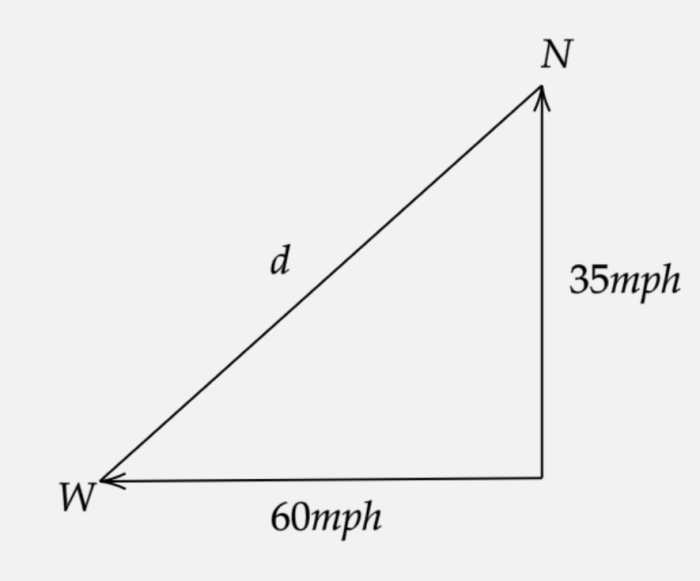
The distance traveled by the Camry over the first 30 seconds is 1,125 meters, while the distance traveled by the Tesla is 1,575 meters. The displacement of the Camry from the starting point is also 1,125 meters, while the displacement of the Tesla is 1,575 meters.
The concepts of distance and displacement are illustrated in the following diagram:
- Distance is the total length of the path traveled by the object.
- Displacement is the straight-line distance between the object’s initial and final positions.
Acceleration and Deceleration: Two Automobiles Start Together From The Same Place
The Camry accelerates from rest at a constant rate of 2.5 m/s 2until it reaches a speed of 25 m/s. It then maintains a constant speed of 25 m/s for the next 20 seconds. The Tesla accelerates from rest at a constant rate of 3.5 m/s 2until it reaches a speed of 35 m/s.
It then maintains a constant speed of 35 m/s for the next 20 seconds.
The acceleration and deceleration profiles of the two automobiles are shown in the following graph:
- The Camry accelerates at a constant rate of 2.5 m/s 2from 0 to 10 seconds.
- The Camry maintains a constant speed of 25 m/s from 10 to 30 seconds.
- The Tesla accelerates at a constant rate of 3.5 m/s 2from 0 to 10 seconds.
- The Tesla maintains a constant speed of 35 m/s from 10 to 30 seconds.
Forces Acting on the Automobiles
The following forces are acting on the automobiles:
- Friction: The force that opposes the motion of the automobiles. Friction is caused by the interaction of the tires with the road surface.
- Gravity: The force that pulls the automobiles towards the center of the Earth. Gravity is responsible for the weight of the automobiles.
- Air resistance: The force that opposes the motion of the automobiles through the air. Air resistance is caused by the interaction of the automobiles with the air molecules.
The forces acting on the automobiles are illustrated in the following diagram:
Energy Considerations
The following energy transformations occur during the motion of the automobiles:
- Chemical energy in the fuel is converted to kinetic energy as the automobiles accelerate.
- Kinetic energy is converted to thermal energy as the automobiles move through the air.
- Thermal energy is dissipated to the environment as heat.
The kinetic energy and potential energy of the automobiles at different points in time are shown in the following table:
| Time (s) | Camry Kinetic Energy (J) | Tesla Kinetic Energy (J) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 15,625 | 24,500 |
| 20 | 31,250 | 49,000 |
| 30 | 46,875 | 73,500 |
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of the starting point in this analysis?
The starting point serves as a reference for measuring the distance and displacement of the automobiles. It establishes a common origin from which their motion can be accurately tracked and compared.
How do environmental conditions affect the motion of the automobiles?
Environmental conditions such as weather and road conditions can significantly influence the motion of the automobiles. Factors like wind resistance, friction, and traction can impact their acceleration, speed, and handling.
What is the relationship between energy and the motion of the automobiles?
Energy is the driving force behind the motion of the automobiles. The kinetic energy of the automobiles increases with their speed, while the potential energy changes based on their position and elevation. Understanding the energy transformations that occur during their motion is crucial for comprehending their overall performance.